Custom Domains, DNS
In this section, we plan to provide our understanding of custom domains and DNS. Specifically how these concepts help us access the sites across the internet. To understand these, we’ll go through the following:
- Example Flow of Computers Communicating
- Basic Understanding of IP Address
- Custom Domains and DNS
Example Flow of Computers Communicating
In my mind, computers are thought of as machines that has the ability to perform processes. These processes generate desired such as:
- Displaying the computer screen that you are viewing now
- Performing mathematical computations
- Running complicated algorithms etc., you guys get the point

Computers do not work in Silo’s to generate the desired outputs. Computers need to communicate with other computers. An example flow is as follows:
- Log into a computer, let’s call it
computer_clientand access the browser - Next, you’d want to visit a website – say
blog.shafikwalakaka.com. This is done by entering the domain of the computer in the browser and hitting enter - On hitting enter,
computer_clientneeds to retrieve the relevant details from another computer that contains all the information for displayingblog.shafikwalakaka.com.- Let’s call this
computer_server
- Let’s call this
- For
computer_clientto be able to connect tocomputer_server,computer_clientwould need to know the IP address ofcomputer_server.- IP addresses are how all computers communicate in this world
- IP addresses are a bunch of string that is unique to identifying a computer. For example,
185.199.111.153
- Once the request has been received by
computer_server.computer_servermust reply with a response tocomputer_client. And yes –computer_serverwill need to specify the IP address ofcomputer_clientto return the relevant details.
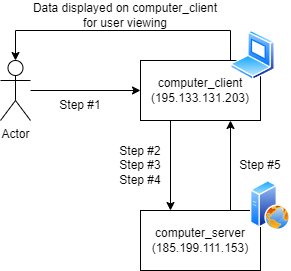
Hold the 5 step process above, and we will tie it all together at the end of this article. The next section will discuss on the mechanism on how computers communicate.
Client and Server
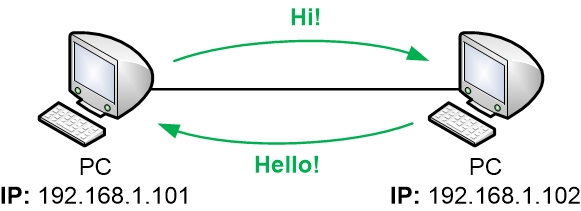
This is the fundamental mode of communication for computers. Similar to humans, when computers communicate, there is always an initator and a recipient. In technical jargon terms:
- The initator of the conversation is referred to as the
client - The recipient of the conversation is referred to as the
server

So the client initiates the request, and the server provides the response.
The above concept is fundamental to understand, before we proceed to the next sections.
Disclaimer – you can also deep dive into what is the content of a request and a response etc. But for now, you can imagine that the client is asking a question and the server is responding with an answer. And both the client and the server are just computers in different locations.
Now we know what clients and servers are, we need to know how they can communicate. There are thousands of computers out there connected to the internet, how does the client specify which server to send the request to?
IP Addresses
IP addresses are unique to each server that is accessible over the internet. IP addresses are how clients specify which server it should reach out to.
IP addresses are a rabbit hole – you can go deep into details such as:
- Who manages the IP addresses
- How are IP addresses assigned
- What are the IP addresses that can be assigned etc.
But for this article, we just need to know that IP addresses are unique strings that are associated with a server. These IP addresses are what clients use when sending a request to a server.
There are two types of IP addresses – IPV4, IPV6
- IPV4 looks like this
185.199.111.153 - IPV6 looks like this
2606:50c0:8000::153
They serve the same purpose - to allow the client to reference a server when they need to communicate, just that there are more IPV6 available (as there are more permutations available due to additional characters).
So taking the earlier example, suppose computer_client wants to retrieve information from computer_server. computer client would need to send a request to an IP address that is associated with computer_server. computer server will reply with a response to the computer_client IP address – the response will contain all the data required to display the blog.shafikwalakaka.com site.
Now that the communication loop is complete, we can further ask – why the need for custom domain name? Since the communication between computers can be completed solely, with IP addresses?
Your IP Address
If you are thinking, it seems that the server needs to know my computer’s IP address. This is technically true. As you are loading this screen, you are computer_client sending request to computer_server for details to show blog.shafikwalakaka.com.
Any outgoing request will include your IP address, so that the server can respond to your accordingly. If you are curious to what is your IP address, you can check it out at the following website – What is my IP?.
You can see your IP addresses displayed below: 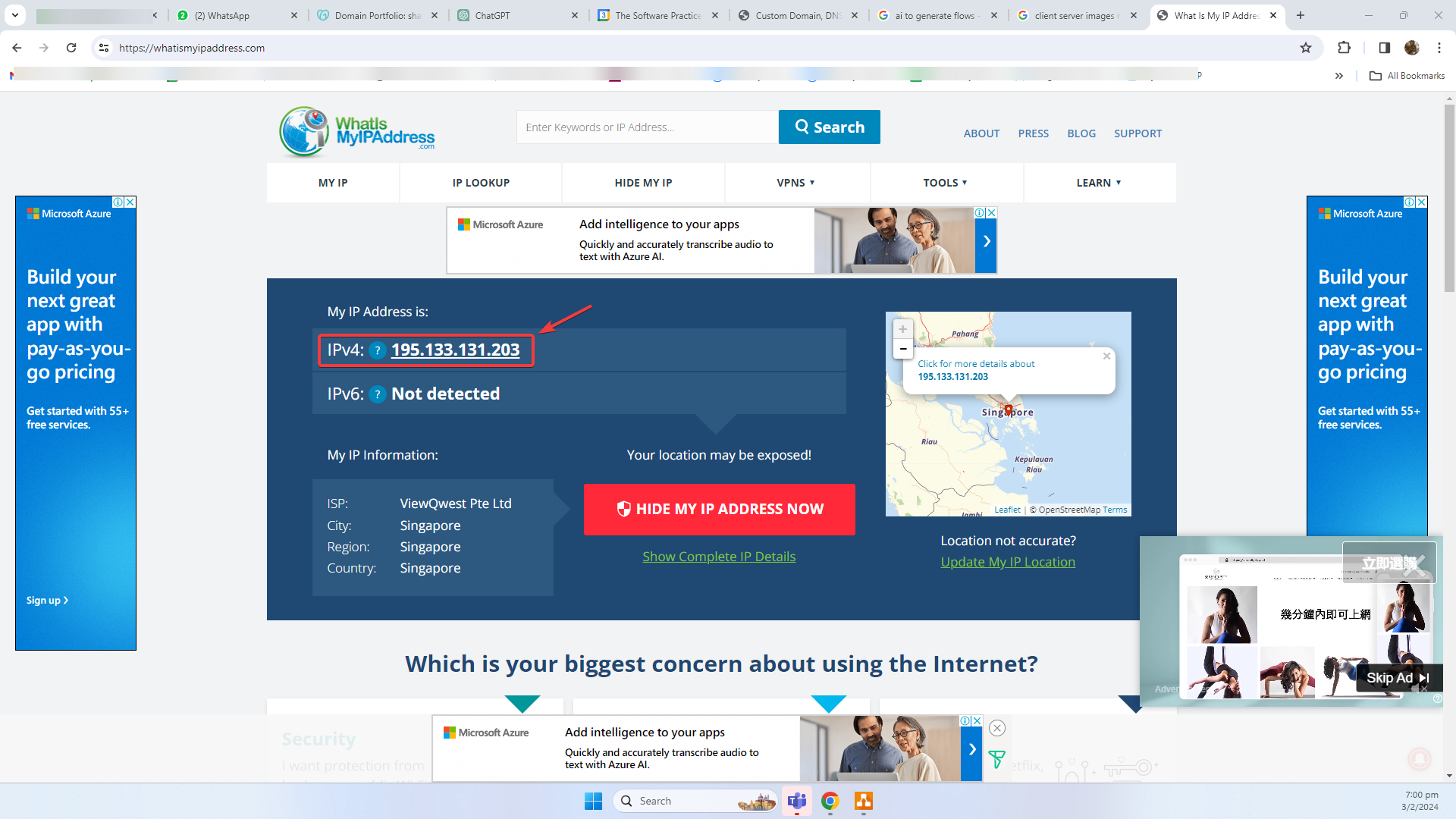
Custom Domains and DNS
Customa Domain names are user friendly strings of text that are actually mapped to IP addresses. This way, users such as you and I do not need to remember the IP addresses of the computer_server.
Taking the above example, suppose blog.shafikwalakaka.com data is stored in computer_server. computer_server has an IP address of 185.199.111.153. It would be very difficult for users to remember 185.199.111.153 everytime they want to visit this blog.
Note: There are multiple sites that users visit and not just the blog. Each site is hosted in a server. Which means each site has an associated IP address. Remembering all these IP addresses would be unbearable and not feasible.
To solve this problem – come custom domain names. In our example, blog.shafikwalakaka.com are custom domain name and can be mapped to IP addresses such as 185.199.111.153.
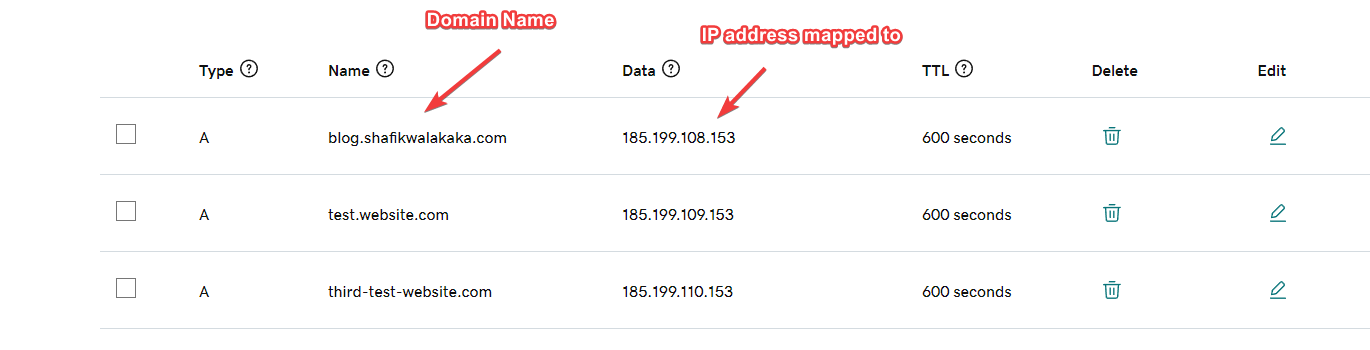
This is handled by the Domain Resolution Service (DNS). These are providers who’s job is to maintain a mapping between the domain name an IP address. Everytime a client is going to make a request to a server, it first reaches out to the DNS service to find the IP address. Once the IP address is ascertained, the client will send the relevant reqeust to the server.
So instead of entering 185.199.111.153, you and I can just simply access the website at blog.shafikwalakaka.com. computer_client will know the IP address 185.199.111.153 based on the domain DNS service, and then send the necessary request to the computer_server.
Putting it Together
Now we go back to the original user requirements – to be able to reach blog.shafikwalakaka.com.
- Log into
computer_client - Access the browser, search for
blog.shafikwalakaka.comand hit enter - The
computer_clientnow checks against the DNS for the IP address ofblog.shafikwalakaka.com- Sends a request to the DNS service for
blog.shafikwalakaka.com - Receives a response that states
185.199.111.153
- Sends a request to the DNS service for
- Now that
computer_clientknows the IP address, it will send a request to185.199.111.153for the website details- Request for website details sent to
185.199.111.153 - Response for website details received from
185.199.111.153
- Request for website details sent to
computer_serverreceives the request and also thecomputer_clientIP address.computer_serverprocesses the requuest and returns the response (which includes all the details to show the site) tocomputer_clientIP addresscomputer_clientnow has all the details to show the site that you are on. It takes the data in the response received, formats it nicely and shows you this nice piece of text for your consumption
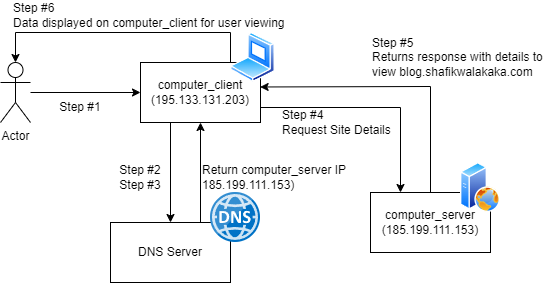
And that’s all folks – just note that there are technical nuances that were skipped and oversimplified above. But the idea is to have a good understanding of how computers communicate.
With this understanding, we’d be able to go one level lower and scrutinize the actual process that actually runs to send, receive and parse this information. But that’s irrelevant for the scope of this article.
Thank you
Thanks for those who reached the end – hope it was useful.
I come from a non-technical background, and was really overwhelmed by the technical jargons. But I realized that once you understand the flow of how it works – they’re really just industry specific jargons that is used to communicate concepts efficiently.
When broken down, the concepts are actually very logical and step-by-step – anyone who is interested in how it works would be able to understand it. But need that geek in you to come out yah
Thank you!
Peace and Love
Shafik Walakaka