Introduction
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Canirox — Web design and implementation notes
- Web building overview
- What we built
- Customisations and files of interest
- Deployment, caching, and performance notes
- Maintenance notes
- Appendix: common selectors to check when updating styles
Canirox — Web design and implementation notes
Canirox is the first human-dog obstacle course event in Singapore. It’s a two-day event with a total of 100 tickets available (50 tickets per day).
Web building overview
We built a website to support discovery, event details, and ticket sales. The site consists of two main user-facing pieces:
- Main landing page — the marketing and information page that introduces the event, shows the schedule, rules, and media.
- WooCommerce checkout — the shopping/checkout flow used to sell tickets and collect attendee details.
Stack
- LAMP-style stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB, PHP) used as the base platform.
- But we did NOT use Apache, We used Litespeed instead
- LiteSpeed web server (note: LiteSpeed is an alternative web server to Apache — it is not a fork of Apache but provides compatibility with many Apache features including reading
.htaccessfiles and supporting mod_rewrite-compatible rules). - WordPress theme: Astra
- Page builder: Elementor (Elementor Pro for custom widgets and theme-builder features)
Note on LiteSpeed vs Apache
LiteSpeed Technologies creates the LiteSpeed Web Server, a drop-in replacement for Apache in most deployment scenarios. It implements compatibility with Apache configuration files (including
.htaccess) and supports common Apache modules behavior (like mod_rewrite) so WordPress and many popular plugins work unchanged. However, LiteSpeed is a distinct web server with its own performance characteristics and additional caching features (LiteSpeed Cache).
What we built
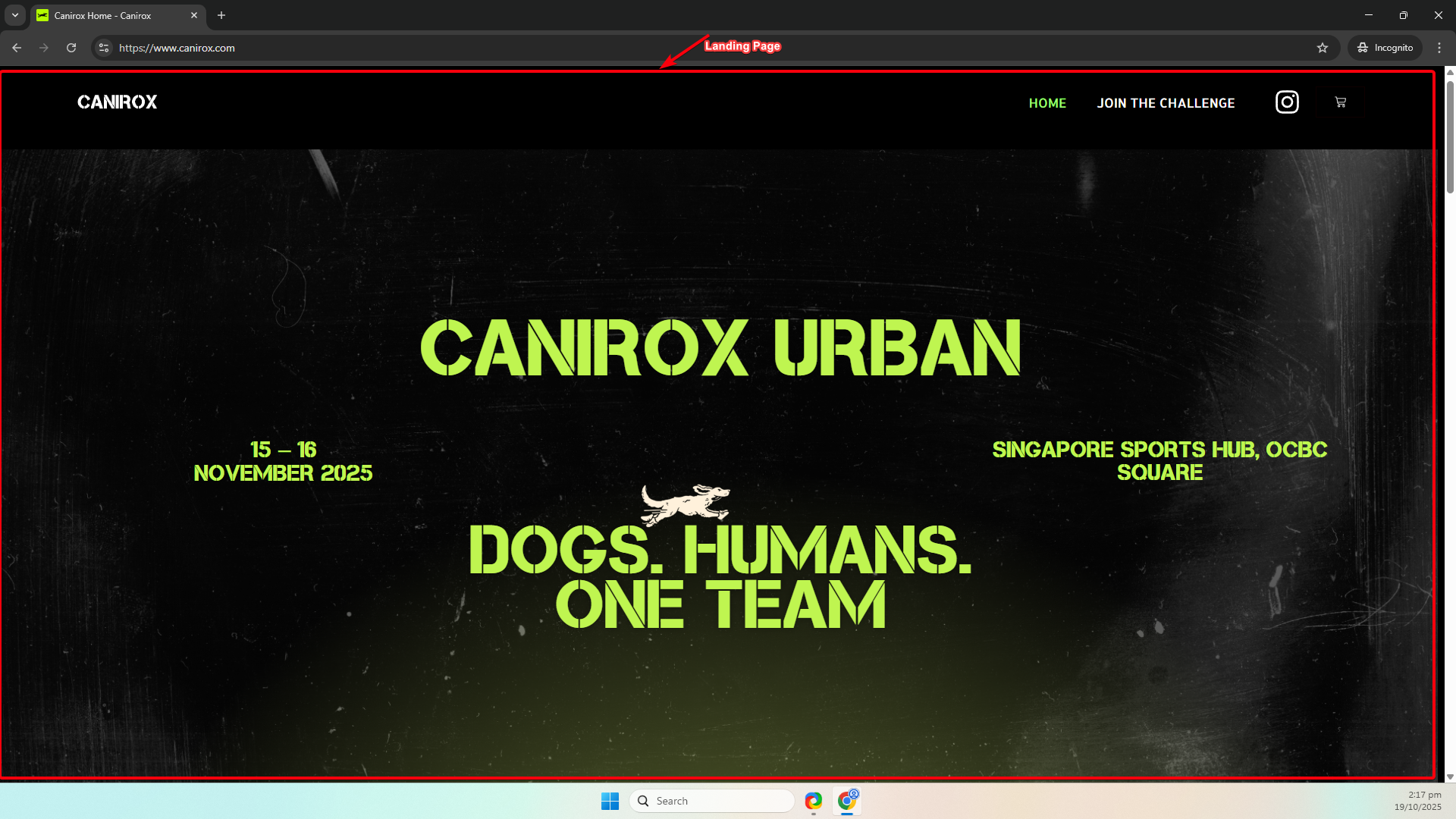
Landing page
- Built with Elementor Pro so marketing pages are easy to author and update.
- Uses custom fonts referenced in the theme’s style CSS. See the project’s
style.cssfor @font-face declarations and fallbacks. - Visual layout and responsive rules are controlled with Elementor global styles plus a few targeted CSS overrides in
extra.css(see below).
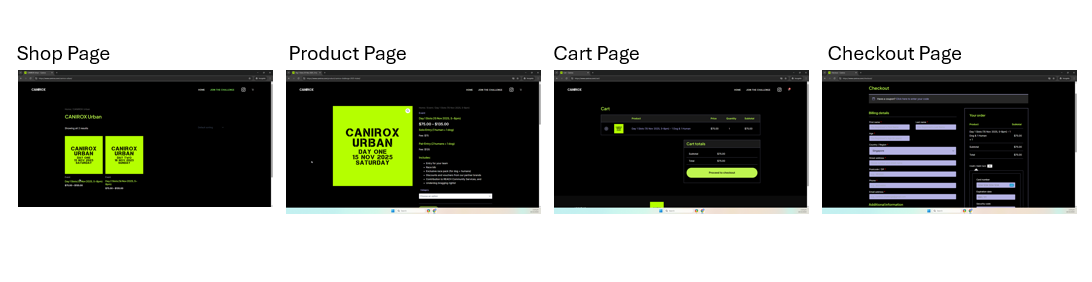
Checkout page (WooCommerce)
- Uses Astra’s out-of-the-box WooCommerce support as the base layout for product and checkout pages.
- Applied additional customisations through the WordPress Customizer and small CSS tweaks in
extra.cssto match branding and improve layout on mobile.
Customisations and files of interest
extra.css — purpose and snippet breakdown
extra.css contains site-specific CSS additions and overrides applied on top of Astra and Elementor outputs. Rather than changing core theme files, these snippets keep custom styles isolated and easy to manage.
Below are common snippet categories and example explanations (adjust selectors to your actual markup):
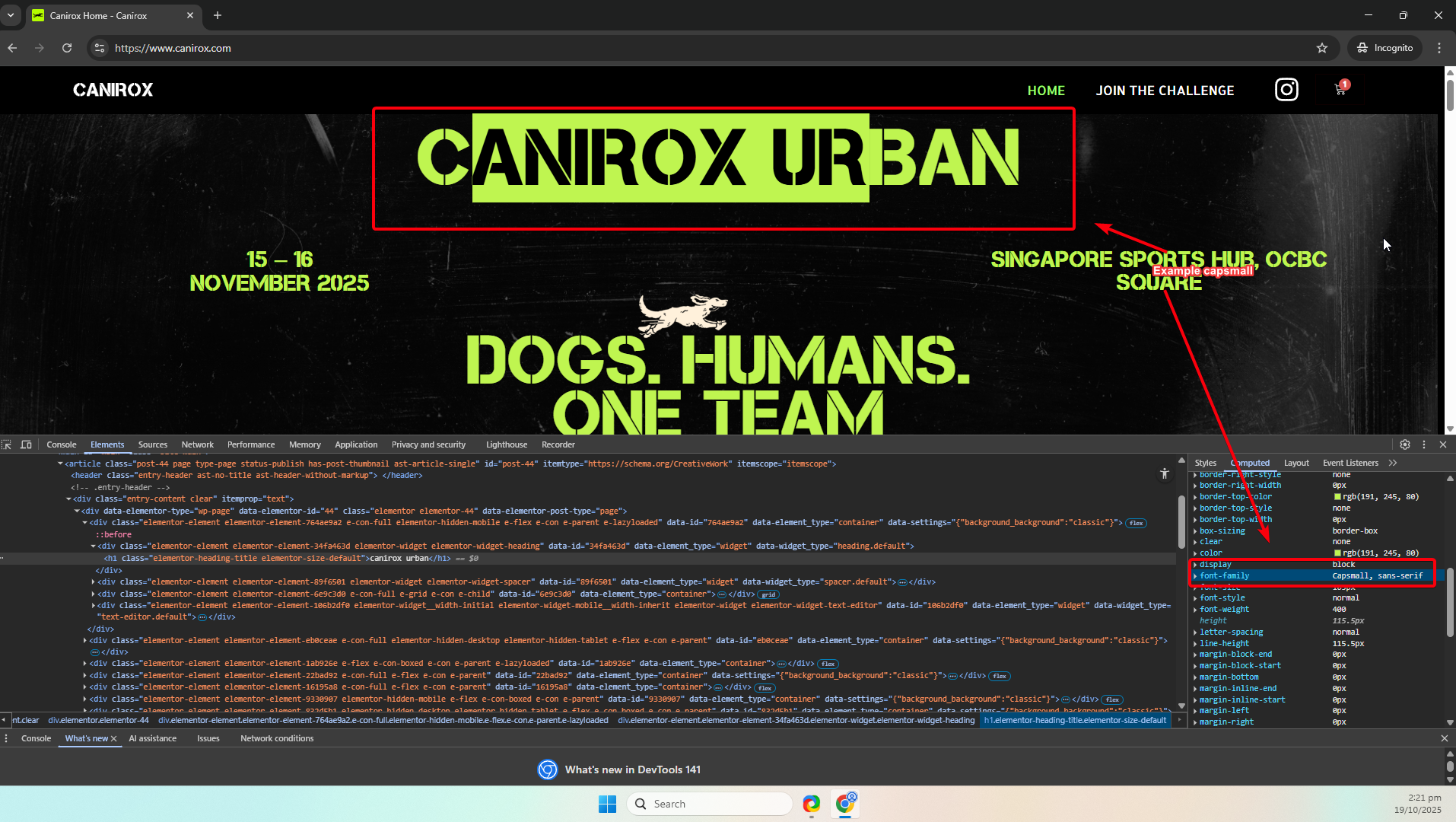
1. Typography and fonts
- Purpose: Ensure brand fonts load correctly and provide fallbacks for accessibility/performance.
parent-page-tech-adventures/child-page-3-wordpress/grandchild-page-14-canirox-web-design/image-1.png
- Example:
/* Actual font declarations from the theme's style.css */ @font-face { font-family: 'Garet Book'; src: url('https://www.canirox.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/garet-book-webfont.woff2') format('woff2'), url('https://www.canirox.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/garet-book-webfont.woff') format('woff'); font-weight: 400; font-style: normal; font-display: swap; } @font-face { font-family: 'Garet ExtraBold'; src: url('https://www.canirox.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/garet-extrabold-webfont.woff2') format('woff2'), url('https://www.canirox.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/garet-extrabold-webfont.woff') format('woff'); font-weight: 800; font-style: normal; font-display: swap; } @font-face { font-family: 'Capsmall'; src: url('https://www.canirox.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/Capsmall_clean.ttf') format('truetype'); font-weight: 400; font-style: normal; font-display: swap; } /* Example usage: set a sensible stack that falls back to system fonts */ body { font-family: 'Garet Book', system-ui, -apple-system, 'Segoe UI', Roboto, 'Helvetica Neue', Arial; } h1, .site-title { font-family: 'Garet ExtraBold', 'Garet Book', Arial; } .caps { font-family: 'Capsmall', Arial, sans-serif; letter-spacing: 0.06em; text-transform: uppercase; } - Why:
font-display: swapprevents invisible text while the font loads and fallbacks keep content readable.
2. Global spacing and container limits
- Purpose: Tighten or expand content width and adjust site spacing to match design.
- Example:
.site-content { max-width: 1100px; margin: 0 auto; } .entry-content p { margin-bottom: 1.15em; } - Why: Astra’s defaults are flexible; we set a max-width so hero sections and content blocks align predictably.
3. Landing page hero and CTA styles
- Purpose: Styling the hero section (background image, overlay, CTA button styles).
- Example:
.hero { background-image: url('/wp-content/uploads/hero.jpg'); background-size: cover; background-position: center; padding: 6rem 0; } .hero .btn-primary { background-color: #E94E1B; border-radius: 6px; } - Why: Visually separates the hero and reinforces the brand color on the call-to-action.
4. WooCommerce / Checkout tweaks
- Purpose: Improve readability and layout of the checkout fields and order summary, and ensure mobile friendliness.
- Example:
.woocommerce-checkout .form-row { display: block; width: 100%; } .woocommerce-checkout .order-review { background: #fff; padding: 1rem; border-radius: 6px; } .woocommerce .woocommerce-message { background: #f6fff4; border-left: 4px solid #67c23a; } - Why: Astra + WooCommerce layout can be wide — these rules keep the checkout compact and scannable.
5. Utility helpers and responsive fixes
- Purpose: Fix small layout bugs introduced by plugins or adjust specific Elementor widgets on mobile.
- Example:
.no-mobile-padding { padding-left: 0; padding-right: 0; } @media (max-width: 768px) { .hero { padding: 3rem 1rem; } .desktop-only { display: none; } }
6. Accessibility and focus states
- Purpose: Ensure interactive elements have visible focus outlines and meet contrast requirements.
- Example:
a:focus, button:focus { outline: 3px solid rgba(233,78,27,0.25); outline-offset: 2px; }
7. Minor animations (kept small and performant)
- Purpose: Add subtle micro-interactions to buttons or section reveals without heavy JS.
- Example:
.btn-primary { transition: transform .12s ease, box-shadow .12s ease; } .btn-primary:active { transform: translateY(1px); }
How extra.css is loaded
- Typically added via the child theme
functions.php(wp_enqueue_style) or via a theme/customizer option that injects additional CSS. - Keep the file small and cache-friendly; for large style sets consider compiling and versioning with build tools.
Annotated extra.css snippets (practical examples)
Below are concrete extra.css snippets you can place in an extra.css file (or the child theme) with annotated comments explaining why each is used and the visual aim.
1) Font loading fallbacks + small performance tweak
/* Ensure custom fonts have a fallback and avoid FOIT (Flash of Invisible Text) */
html { font-family: 'Garet Book', system-ui, -apple-system, 'Segoe UI', Roboto, 'Helvetica Neue', Arial; }
/* If the custom font is slow, swap to system fonts immediately for better perceived performance */
Aim: Keep text readable while fonts load, and ensure headings use the brand font when available.
2) Hero section visual polish
/* Big hero with image, subtle dark overlay for contrast with white CTA */
.hero {
background-image: url('/wp-content/uploads/hero.jpg');
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
position: relative;
padding: 6rem 0;
}
.hero::before {
content: '';
position: absolute;
inset: 0;
background: linear-gradient(rgba(0,0,0,0.18), rgba(0,0,0,0.18));
pointer-events: none;
}
.hero .btn-primary { background-color: #E94E1B; border-radius: 6px; }
Aim: Improve legibility over background images and emphasize the CTA color.
3) Checkout and order summary layout
/* Make checkout fields stack cleanly and make the order summary readable */
.woocommerce-checkout .form-row { display: block; width: 100%; }
.woocommerce-checkout #order_review { background: #fff; padding: 1rem; border-radius: 6px; box-shadow: 0 1px 3px rgba(0,0,0,0.06); }
.woocommerce-checkout .woocommerce-billing-fields .form-row-first,
.woocommerce-checkout .woocommerce-billing-fields .form-row-last { width: 48%; display: inline-block; }
@media (max-width: 680px) {
.woocommerce-checkout .woocommerce-billing-fields .form-row-first,
.woocommerce-checkout .woocommerce-billing-fields .form-row-last { width: 100%; display: block; }
}
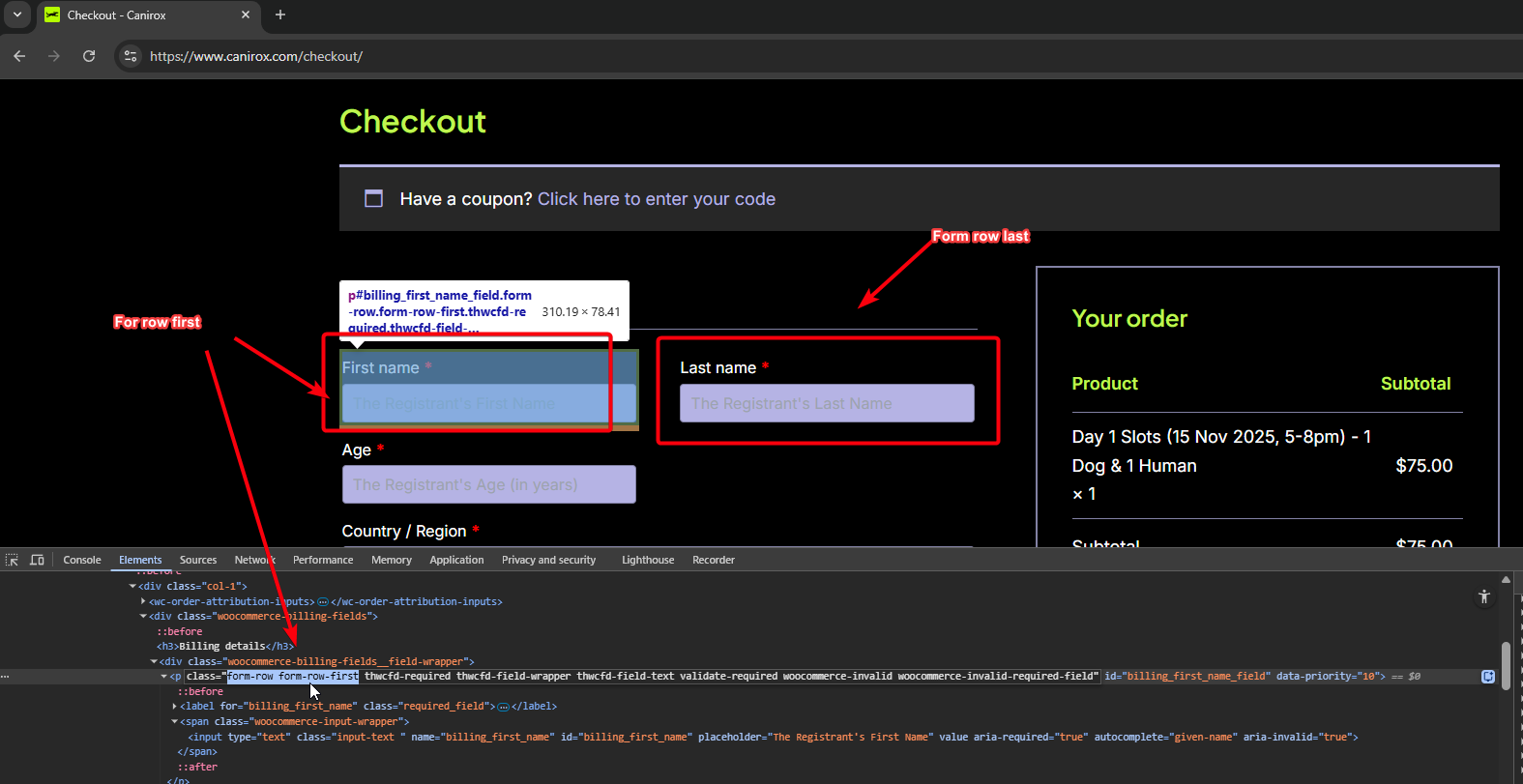 Aim: Keep form inputs aligned on desktop but stack cleanly on mobile. Improve visual separation of order summary.
Aim: Keep form inputs aligned on desktop but stack cleanly on mobile. Improve visual separation of order summary.
4) Minor alignment and spacing helpers
/* Utility classes for quick adjustments */
.no-mobile-padding { padding-left: 0 !important; padding-right: 0 !important; }
.center-cta { text-align: center; }
.small-meta { font-size: 0.9rem; color: #666; }
Aim: Reusable helpers to fix layout issues originating from different plugin markup.
5) Accessibility & focus styles (important for keyboard users)
a:focus, button:focus { outline: 3px solid rgba(233,78,27,0.25); outline-offset: 2px; }
.btn-primary:focus { box-shadow: 0 0 0 3px rgba(233,78,27,0.15); }
Aim: Make keyboard navigation visible and keep contrast for accessibility.
6) Small performance-conscious animations
.btn-primary { transition: transform .12s ease, box-shadow .12s ease; }
.btn-primary:active { transform: translateY(1px); }
Aim: Add subtle feedback on interaction without heavy JavaScript.
7) Specific overrides you may already have in extra.css
/* Example: reduce oversized margins introduced by some Elementor widgets */
.elementor-section .elementor-container { max-width: 1200px; margin-left: auto; margin-right: auto; }
/* Example: normalize button styles across Astra and Elementor */
.button, .ast-button, .elementor-button { border-radius: 6px; padding: 0.65rem 1.1rem; }
Aim: Normalize spacing and control the look of buttons and containers across theme and builder outputs.
Deployment, caching, and performance notes
- Since the site runs on LiteSpeed, use LiteSpeed Cache plugin for WordPress to take advantage of server-level caching and HTML object caching.
- Exclude the checkout and cart pages from full-page caching. Keep cart, checkout, and account pages dynamic.
- Use server-level or CDN caching for static assets with long cache TTL and versioned URLs for cache-busting when styles change.
Maintenance notes
- Keep WordPress, Astra, Elementor (and Elementor Pro), and WooCommerce up to date.
- Test major upgrades on a staging site before pushing to production, especially for payment/checkout flows.
- Monitor error logs and the shop’s email notifications to confirm orders are being created and payments recorded.
Appendix: common selectors to check when updating styles
.site-header,.site-footer,.hero,.entry-content,.woocommerce-checkout,.woocommerce .product,.elementor-widget,.astra-button